Nissan Engineering Standard – Salt Spray Testing
Nissan MES-M0007 is used to measure the degree of rusting, blistering and adhesion when the specimen is exposed to corrosive conditions such as salt spray, drying and wetting (condensate humidity)
Method A of the standard requires salt spray testing in accordance with NES M-0140 whereby test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5 to 7.2) salt water solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1.0 to 2.0ml/80cm²/hour, in a chamber temperature of +35C. This climate is maintained under constant steady state conditions. The test duration is variable.
This test is also referred to as an NSS test.
Salt spray corrosion test used to test the effectiveness of corrosion protection systems
Can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of metallic materials with or without temporary or permanent corrosion protection, when exposed to a salt spray climate (neutral salt spray or acetic acid salt spray or copper accelerated acetic acid salt spray) at an elevated temperature.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of CASS Solution (pH 3.1 to 3.3) Salt concentration: 50 + 5 g/l Copper(II) chloride . 2H2O: (0.26+/- 0.02) g/l. Which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 30 to 40 ml/80cm²/24 hours, in a chamber temperature of +35°C or +50°C. This climate is maintained under constant steady state conditions. The test duration is variable. The chamber should not be filled to more than 50% capacity.
In all other respects this test is based upon ISO 9227.
For further information on ISO standards visit; www.iso.org
Note: many ISO test standards have been harmonized with other European standards and these are now prefixed ‘EN’ (Euro Norm) or ‘** EN’ – where ** are the letters representing a European country/language code, for example ‘BS EN’ for a harmonized British standard in English language.
Salt spray corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres
EN 13523-8 can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of metallic materials with or without temporary or permanent corrosion protection, when exposed to a salt spray climate (neutral salt spray or acetic acid salt spray or copper accelerated acetic acid salt spray) at an elevated temperature.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5 to 7.2) or acidified (pH3.1 to 3.3) salt water solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1.0 to 2.0ml/80cm²/hour, in a chamber temperature of +35C. This climate is maintained under constant steady state conditions. The test duration is variable.
EN 13523-8 tests are also referred to as a NSS, ASS & CASS tests.
For further information on EN 13523-8
Please contact us via contact page
In recent years the automotive industry has been faced with many technical challenges in attempting to comply with a series of industrial norms. One of the most important of these norms is LV 124, which was jointly developed by a group of German automobile manufacturers; Daimler Benz, Audi, BMW, Volkswagen, and Porsche.
Most of these manufacturers have now developed their own version of this standard, these include Mercedes (MBN LV 124-1), BMW(GS 95024-2-1), and VW (VW 80000).
This complex 160 page standard covers test procedures for electrical and electronic components in passenger motor vehicles weighing less than 3.5 tonnes, and includes electrical tests, mechanical tests, climatic tests, and service life tests.
Amongst the many individual tests within the standard is a requirement for corrosion testing, this element of LV 124 is based upon EN 60068-2-11, which is undertaken to test the resistance of the component to malfunction when exposed to a salt spray climate at an elevated temperature, due to short circuits and leakage currents caused by ingress of salt into the component.
Electronic & electrical component parts: Salt Spray (Corrosion)
Can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated and uncoated specimens, when exposed to a salt spray climate at an elevated temperature.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5 to 7.2) salt water solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 0.5 to 3.0ml/80cm²/hour, in a chamber temperature of +35C. This climate is maintained under constant steady state conditions. The test duration is variable.
For further information on VG standards visit; www.global.ihs.com
Test method for resistance to salt fog (Jaguar)
TPJLR.52.252
This Jaguar automotive test standard is based upon test standard ASTM B117. Please see elsewhere in this document for details of ASTM B117.
Corrosion Test in artificial atmospheres – salt spray tests
This Volvo automotive test standard is the same as ISO 9227 (Salt spray corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres). Click here to view details of the ISO 9227 standard test.
For further information on Volvo standards visit; volvogroup.com/suppliers
Environmental Conditions & Test Procedures for Airborne Equipment – Section 14; Salt Spray
This ‘Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics’ test standard had been revised and re-issued several times, with each issue being designated a new sequential suffix letter, which appears after the main standard number. With each revision the section number specific to this particular test may have changed, but the method itself is generally as follows:
Can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of equipment, when exposed to a salt spray climate at an elevated temperature.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5 to 7.2) salt water solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 0.5 to 3.0ml/80cm²/hour, in a chamber temperature of +35C. This climate is generally maintained under constant steady state conditions, but may also be cycled between salt spray for 24 hours and ambient air drying for 24 hours. The test duration is variable.
For further information on RTCA Inc. standards visit; www.rtca.org
Protection against physical & biological agents: Salt spray test
Can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated and uncoated metallic specimens, when exposed to a salt spray climate at an elevated temperature.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5 to 7.2) salt water solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 1.0 to 3.0ml/80cm²/hour, in a chamber temperature of +35C. This climate is maintained under constant steady state conditions. The test duration is variable.
For further information on French standards visit; www.afnor.fr
Environmental engineering considerations & laboratory tests: Salt fog
This MIL standard has been revised and re-issued several times, with each issue being designated a new sequential suffix letter, which appears after the main standard number. With each revision the method number specific to this particular test may have changed, but the method itself is generally as follows:
Can be used to test the relative resistance to corrosion of coated and uncoated specimens, when exposed to a salt spray climate at an elevated temperature.
Test specimens are placed in an enclosed chamber and exposed to a continuous indirect spray of neutral (pH 6.5 to 7.2) salt water solution, which falls-out on to the specimens at a rate of 0.5 to 3.0ml/80cm²/hour, in a chamber temperature of +35C. This climate is generally maintained under constant steady state conditions, but may also be cycled between salt spray for 24 hours and ambient air drying for 24 hours. The test duration is variable.
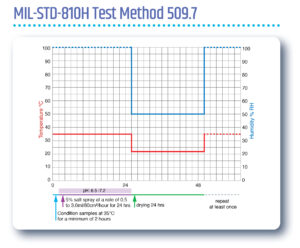
Notes:
1. At least two hours of pre-conditioning are required at the test temperature before commencing the salt spray test.
2. Test samples need to be dried periodically at “standard ambient temperatures and a relative humidity of less than 50% for 24 hours, or as otherwise specified”.
Unless a fully automatic and multi-environment test chamber is utilised, the above requirements imply significant manual intervention during this test, including the use of supplementary controlled environment chambers.
For further information on US Dept of Defence MIL standards visit; www.nssn.org
