Salt Spray Testing — Complete Guide
Salt spray testing, also known as salt fog testing or corrosion testing, is a widely used method to evaluate the corrosion resistance of metals, coatings, and finished products. This guide covers everything you need to know, from test types and standards to procedures, applications, and FAQs.
What is Salt Spray Testing?
Salt spray testing is a laboratory procedure used to simulate a corrosive environment to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings. By exposing test specimens to a controlled salt fog (usually sodium chloride solution), manufacturers can assess how long a product can withstand corrosion before visible deterioration occurs.
Applications include:
-
Automotive parts
-
Coated metals
-
Electronics and fasteners
-
Aerospace components
How Does Salt Spray Testing Work?
Salt spray chambers create a humid, saline environment where the test specimen is continuously exposed to a fine mist of salt solution. Over time, corrosion forms on susceptible materials, allowing engineers to:
-
Evaluate coating quality
-
Identify weak points in materials
-
Compare performance between products or coatings
Key parameters include:
-
Salt solution concentration (commonly 5% NaCl)
-
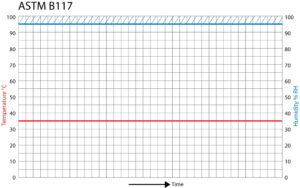
Temperature (typically 35°C / 95°F) although some tests such as ISO 9227 require 50°C / 122°F
-
Duration of exposure (hours to hundreds of hours)
Types of Salt Spray Tests
1. Neutral Salt Spray (NSS)
-
Most common test type
-
Uses neutral pH (6.5–7.2) sodium chloride solution
-
Standard for evaluating corrosion resistance of painted or coated metals
2. Acetic Acid Salt Spray (AASS)
-
Uses acidic solution (pH ~3.1–3.3)
-
Accelerates corrosion, especially for zinc coatings
-
Common in automotive and galvanization testing
3. Copper Accelerated Acetic Acid Salt Spray (CASS)
-
Contains copper chloride and acetic acid
-
Highly aggressive test for plated metals
-
Evaluates protective coatings in harsh conditions
What Are Salt Spray Testing Standards?
Several international standards govern salt spray testing, including:
| Standard | Scope | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B117 | Neutral salt spray test | General metal corrosion testing |
| ISO 9227 | Salt spray testing guidelines | Coatings and industrial applications |
| ASTM G85 | Modified salt spray tests | Cyclic corrosion for automotive |
| ASTM D117 | Paint and coating corrosion tests | Coating performance evaluation |
How Long Does Salt Spray Testing Take?
Salt spray testing duration depends on the material and coating type:
-
Mild steel: 24–48 hours to see corrosion
-
Coated metals: 96–500+ hours depending on coating quality
-
High-performance coatings: up to 1000 hours for automotive or aerospace
Tip: Testing should be aligned with the intended standard for accurate benchmarking.
Can Salt Spray Testing Predict Real-World Corrosion?
Salt spray testing provides accelerated corrosion data. While it’s excellent for comparing coatings, it does not exactly replicate natural corrosion conditions, which are affected by:
-
UV exposure
-
Temperature cycling
-
Humidity fluctuations
-
Pollutants (Such as SO2 Gas)
For realistic predictions, cyclic corrosion testing (CCT) or field exposure may be required.
Salt Spray Testing Procedure — Step by Step
-
Prepare Specimens
Clean and weigh specimens; apply coatings as needed.
-
Set Up Chamber
Fill with 5% NaCl solution (or specific solution for test type)
Adjust temperature to 35°C ± 2°C -
Install Specimens
Place specimens at a 15–30° angle to allow solution runoff. -
Start the Test
Spray chamber continuously, monitoring solution concentration and pH. -
Inspect Specimens
At intervals (e.g., 24, 48, 96 hours), check for corrosion spots, pitting, or coating failure. -
Document Results
Record hours to first visible corrosion, type of corrosion, and appearance.
Common Salt Spray Testing FAQs
What materials can be tested in a salt spray chamber?
Metals, alloys, coated metals, plastics with metallic finishes, and fasteners.
How do I interpret salt spray test results?
Compare corrosion onset and severity against the applicable standard or specification.
How often should salt spray chambers be maintained?
Monthly cleaning, solution replacement every 4–6 weeks, and routine calibration of temperature and spray rate.
Is salt spray testing suitable for automotive coatings?
Yes, it is widely used for pre-production testing, but cyclic corrosion testing is more accurate for predicting real-world performance.
Why Choose Ascott Analytical ?
At Ascott Analytical, we provide:
-
We bring Over 37 years of experience in knowledge on corrosion topics
-
Wide range of chambers to suit your application
-
Excellent customer service with quick response times
-
Tailored solutions to customize testing conditions to meet your specific requirements and industry standards.
Contact us today to discuss your testing requirements and ensure your products meet industry standards.